supraspinatus partial tear test|incomplete full thickness tear supraspinatus : bespoke Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. Resultado da 20 de mar. de 2020 · No vídeo especial de Natal, em que eles fazem a tradicional sobremesa rabanada, feita à base de pão e que leva ovo, leite condensado e leite, além de açúcar e canela, Geisy e Kid alcançaram 756 mil views até o momento. Como o vídeo segue no ar, o contador é .
{plog:ftitle_list}
28 de jan. de 2023 · Traduzido por HIGOR (Twitter): https://twitter.com/guardioesmlb_br?s=21&t=0oeu-WDg8EDyR9ZZsPGPPQ ️EPISÓDIOS COMPLETOS DA .
Partial rotator cuff tears are common in people who are overhead athletes (they play sports with an upper arm and shoulder arc over the head), such as pitchers in baseball. Partial rotator cuff .
Patients will present with shoulder pain and tenderness along the supraspinatus tendon. Many might present with a limited range of motion, especially in abduction. The Jobe test can be performed to elicit any injury to .
Partial thickness tears of the supraspinatus muscle are an incomplete disruption of muscle fibers; note that these can progress to a complete or full thickness tear of the supraspinatus muscle, and larger tears .The sulcus sign, the relocation test, and the degrees of anterior and posterior humeral translations, . Middleton W, Yamaguchi K. Tendon integrity and functional outcome after . Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X .
supraspinatus tear test pdf
Description. When one or more of the rotator cuff tendons is torn, the tendon becomes partially or completely detached from the head of the humerus. In most rotator cuff tears, the tendon is torn away from the bone. Most tears occur in .
Front view (left) and overhead view (right) of the tendons that form the rotator cuff. The blue arrows indicate a full-thickness tear in the supraspinatus tendon, the most common location for rotator cuff tears. Partial-thickness tears are described as either articular sided or bursal sided, with articular-sided tears being two to three times more common. Tear size is described as .
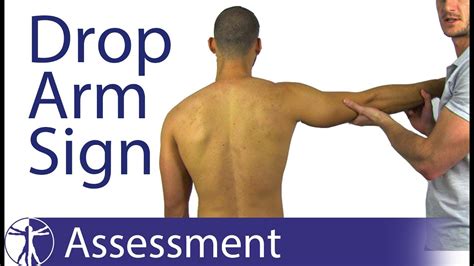
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body. . Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
special tests for supraspinatus tear
The Neer sign and the Hawkins-Kennedy sign, commonly used to diagnose subacromial impingement, have a high sensitivity of 75–88% for supraspinatus tears.[18,19,20,21] However, these signs are characterized by a lack of specificity (<40%).[20,21] The transdeltoid palpation test, first described by Codman in 1934, has been used to diagnose .
A tear of the supraspinatus tendon can be detected by the empty-can test (Fig. 8) or full-can test (Fig. 9) . The accuracy of the tests was the greatest when muscle weakness was interpreted as indicating a torn supraspinatus tendon in both the full-can test (75 % accurate) and the empty-can test (70 % accurate) [ 13 ]. The rotator cuff is an anatomic coalescence of the muscle bellies and tendons of the supraspinatus (SS), infraspinatus (IS), teres minor (TM), and subscapularis (SubSc) surrounding the shoulder joint (see Image. Shoulder Joint Anatomy).[1] Rotator cuff syndrome constitutes a spectrum of diseases across various pathologies associated with injuries or degenerative .Purpose: The purpose of this study was to analyze the diagnostic value of 7 clinical tests for the diagnosis of supraspinatus tendon tears, to investigate the ability of these tests to distinguish between partial- and full-thickness tears, and to compare 3 different ways of interpreting positive test results (weakness and pain): (1) in case of pain, (2) in case of weakness, regardless if with . c because of pain in the right shoulder. Although she had never experienced trauma and had not overused her shoulder and arm, the patient showed limited range of motion with painful arc syndrome. Moreover, the Neer test and Hawkins–Kennedy test were positive with subacromial tenderness. Diagnoses: The MRI findings revealed partial tears on the articular .
shoulder tests for rotator cuff
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B. Older age: This can cause the deterioration of tendons due to long-term wear and tear.; Acute trauma: Examples include a severe fall or a blow to the shoulder during sports.; Repetitive stress injury: This is caused by the overuse of the shoulder during sports (like tennis, baseball, volleyball, rowing, and swimming) or by jobs that require you to lift heavy objects or .
Supraspinatus tendon disorders have been classically described as degenerative processes starting from an acute tendinitis, progressing to tendinosis, and eventually resulting in partial or full thickness tendon rupture. 29-29 However, currently the terms tendinitis and tendinosis should be avoided and the word tendinopathy should be preferred .Supraspinatus is the smallest of the 4 muscles which comprise the Rotator Cuff of the shoulder joint specifically in the supraspinatus fossa. . along with the Full Can Test is a commonly used orthopedic examination test for supraspinatus impingement or integrity of the supraspinatus muscle and tendon. The test is usually easier in sitting or .
If acute rotator cuff tear caused by trauma is suspected (trauma, pain, and weakness). Ideally, the person should be seen in the next available specialist shoulder clinic. Basis for recommendation
Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. Ultrasound. This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. It allows a provider to assess the .Treatment for a supraspinatus tendon tear will often be determined by the severity of the tear and how it is impacting your day-to-day activities. Partial thickness tears, where only a portion of the tendon is torn, can often be addressed with conservative and non-surgical treatments such as rest, ice, physical therapy, and medications may be .The four muscles — supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor — originate from the scapula (shoulder blade). The rotator cuff tendons attach to the head of the humerus in bony spots referred to as the greater and lesser .Most commonly tears are described as partial- or full-thickness. A commonly cited classification system for full- thickness rotator cuff tears was developed by Cofield (1982). The classification system is: 1. Small tear: less than 1 cm .
Subacromial bursitis, rotator cuff tendinitis, and partial rotator cuff tears cause shoulder pain, especially when the arm is moved overhead. The pain usually is worse between 60 ° and 120 ° (painful arc of motion) of shoulder abduction or . The majority of people with pain due to partial supraspinatus tears will respond very well to physical therapy. . suspected a labral tear as well but didn’t want to do an arthogram as he felt there was no need for the invasive test if we weren’t doing surgery. I’ve been doing PT almost daily now since March 14th and range of motion is . Most partial thickness rotator cuff tears fall into one of three grades, based on their severity. In Grade 1, the tear is only about 3 millimeters deep. In Grade 2, it’s deeper (between 3 to 6 mm), . Test Yourself for Supraspinatus Tear. There are some tests, however, that you can perform yourself to see if your supraspinatus is involved . Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of tests and imaging techniques
shoulder supraspinatus test

The same study suggested that the full can test was unable to determine between partial thickness and full thickness tears of the supraspinatus tendon. The full can test also showed better diagnostic value and higher correlation with intraoperative results for tears at least 1 cm in size. It is however, questionable on the value that the . ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎ ︎ http://bit.ly/GETPT ︎ ︎OUR APPS: 📱 iPhone/iPad: https://apple.co/35vt8Vx🤖 Andro.
Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the .
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: Diagnosis and Treatment - TeachMe Orthopedics Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: Diagnosis and Treatment - TeachMe Orthopedics . an acronym for a partial articular supraspinatus tendon avulsion. These are the injuries that will be discussed more thoroughly in this chapter . Another test that may be . Stage 0 is an intact rotator cuff, stage IA is a partial-thickness tear of the supraspinatus, and stage IB is a full-thickness tear involving only the supraspinatus. Stage II includes the supraspinatus and a portion of the infraspinatus. Stage III includes the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis tendons. - Drop arm test; Pictures - Painful arc sign for . (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor) stabilize the glenohumeral . (extending completely from the articular to the bursal surface) or partial thickness. Partial-thickness tears are described as either articular sided or bursal sided, with articular-sided tears being .
Type of supraspinatus tear: Chi-Squared test: Variables: N: Normal/no tear (N = 119) Partial tear (210) Complete tear (N = 143) Tendinopathy (208) Value (X 2) df: P value: Gender: 680: 34.719: 3 . However, calcific tendinitis and partial supraspinatus tears should be closely monitored, as the symptoms of one may mask the other, preventing .
incomplete full thickness tear supraspinatus
full thickness tear supraspinatus
WEBXNXX.COM 'gemendo cdzinha' Search, free sex videos. Language ; Content ; Straight; Watch Long Porn Videos for FREE. Search. Top; A - Z? . Paula CDzinha. .
supraspinatus partial tear test|incomplete full thickness tear supraspinatus